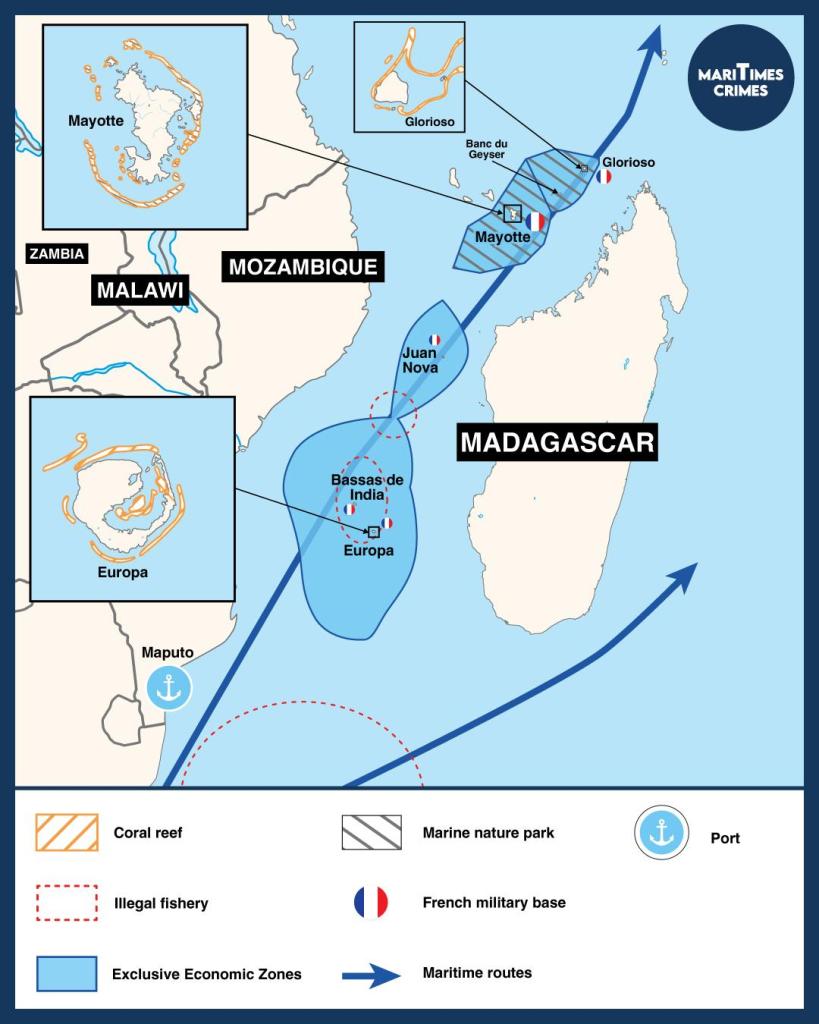
The Mozambique Canal is one of the most used international shipping routes. Situated between the Mozambique, Madagascar and Comoros archipelagos, the canal represents 30% of the petrol traffic and 5000 ships per year use this route. The Mozambique Canal is also located in an area with four geological reserves of hydrocarbons and minerals, which are being exploited by several actors, and can count on the presence of France to stabilise the region.
Mayotte, La Réunion and the Scattered islands in the Indian Ocean make up the French territory in the Mozambique Channel. This French presence constitutes a large EEZ and positions France as a key player in the region.
France a key player
With 434100 km of EEZ and 42 km of islands, France is a significant player in the region. The scattered islands are at the centre of the Canal, Bassas da India, Europa and Juan de Nova. Thanks to the Montego Bay Convention, France exercises its jurisdiction and sovereignty over its territory and works to maintain the safety and environmental preservation of the maritime spaces.
French presence as protector of a fragile ecosystem
The Mozambique Channel is a rich area and is full of diverse ecosystems, it’s the second hotspot of marine biodiversity tropicale on the planet. The scattered islands are famous to habited a numerous community of vegetales such as phanerogam meadows mainlt oresent in the Glorioso deep sea, mangovres which offers habitat to birds and turtles. In addition, corals, algae, play an important role for the biodiversity of the region, as terrestrial as maritimes.
In fact, the Banc du Geysir, is known for its exceptional patrimonial, including green turtles and also 1 338 species of which 13% are endangered, either present under the Nairobi Convention and the CITIES. The archipelago of the Glorioso is a species sanctuary and a refuge for biodiversity, as fishing is illegal. In this regard, many species has prolifiels such as sharks, sea cucumbers. It’s also a great reserve for corals, in Juan de Nova, where species on the brink of extinction are presente, it’s the case of the Napoléon and the saddled grouper, which are fishy bones, but also for sharks like the scalloped hammerhead, which is also endangered.
Scientist community
Thanks to the scientific community financed by the European Development Fund, a great deal of work is being done to study and preserve the region’s biodiversity. In fact, the connection between the Scattered islands is important for the reproduction, feeding and migration of species. The islands represent 10% of the specific fish richness of the Indian Ocean. Many of these species are protected by international conventions (International Whaling Commission (IWC), Washington Convention (CITES), Bonn Convention, Nairobi Convention, Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS)…).
For all these reasons, and because of the importance of the region for biodiversity, the French government, through the French Global Environment Facility (FFEM), is working on five priorities The conservation of biodiversity and the improvement or resilience of aquatic ecosystems is one of them and is monitored by a scientific and technical committee and five different committees (economy and finance, foreign affairs, environment, research, agriculture).






